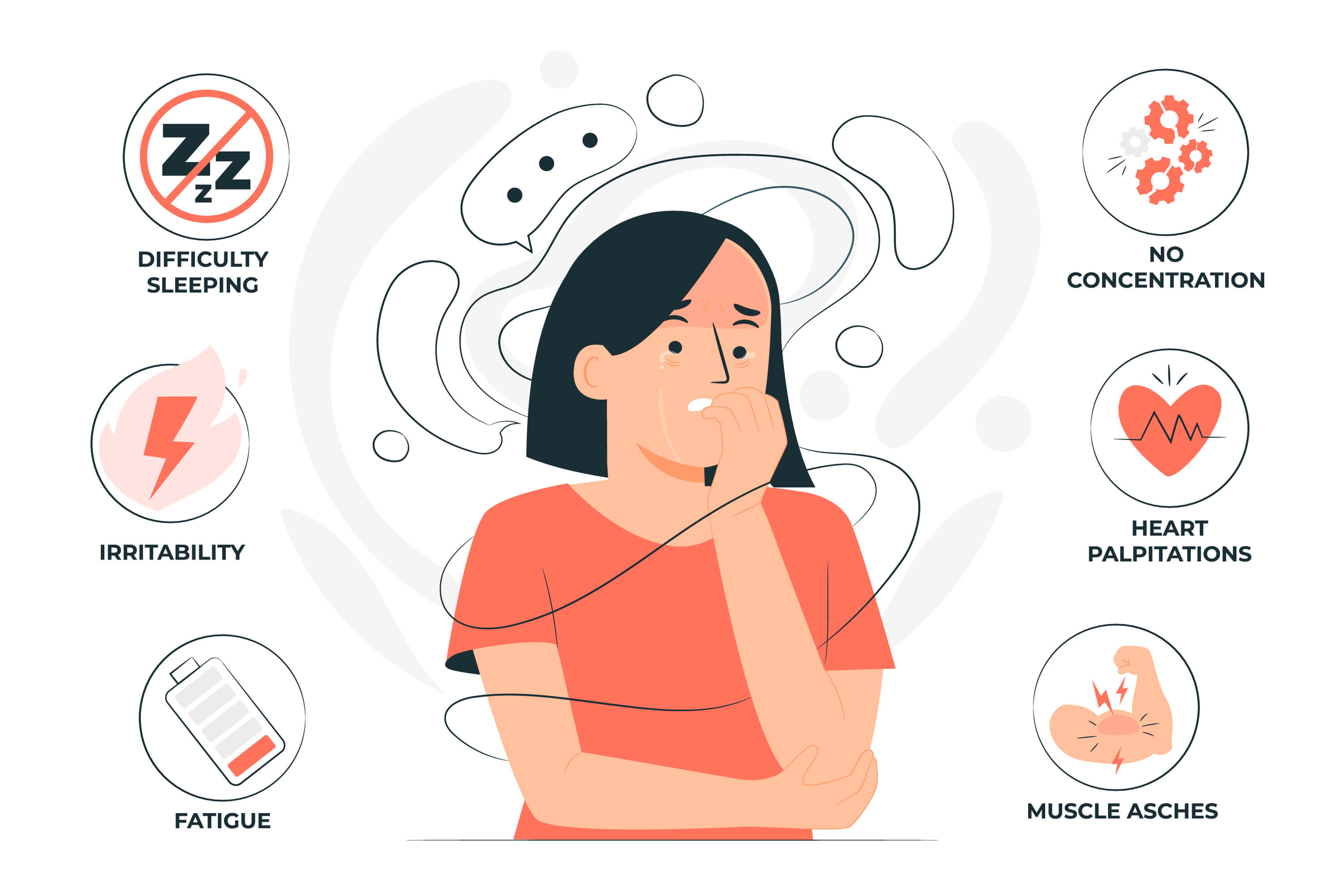
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is one of the most common anxiety disorders, affecting nearly one in eight people in the United States. Individuals with GAD experience persistent anxiety and worry about everyday activities or events for at least six months. They often feel a lack of control over their worry and may be overly concerned about money, health, family, work, or other daily occurrences. The cycle of worry can be challenging to break, leading to increased anxiety and negative impacts on daily life.
Physical symptoms of GAD may include restlessness, fatigue, muscle tension, sweating, accelerated heart rate, stomach issues, trembling, and sleep disturbances. Mental symptoms can involve excessive anxiety or worry, difficulty controlling the worry, a sense of impending danger, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and difficulty remembering things.
Panic Disorder Panic disorder is characterized by sudden and repeated episodes of intense fear, known as panic attacks. These attacks can occur unexpectedly and cause individuals to feel as though they are losing control or experiencing a heart attack. Panic attacks typically last several minutes but can be incredibly distressing. People with panic disorder may develop a fear of having future panic attacks, leading to avoidance behaviors and significant disruptions in their lives.
Physical symptoms of panic disorder may include a rapid heartbeat, sweating, trembling, chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, stomach distress, and feelings of impending doom. Mental symptoms can involve feeling detached from oneself or reality, fear of losing control or dying, and a sense of unreality.
Social Anxiety Disorder Social anxiety disorder, also known as social phobia, is characterized by an intense fear of being judged, embarrassed, or humiliated in social situations. People with social anxiety disorder often experience significant distress and anxiety in social gatherings or when they anticipate social interactions. They may avoid social situations altogether, leading to isolation and difficulties in forming relationships.
Symptoms of social anxiety disorder may include fear or anxiety about social situations, shyness or withdrawal in social settings, blushing, sweating, being closed off in conversation, trembling, poor eye contact, and fear of speaking in front of others.
Separation Anxiety Separation anxiety is a normal part of development, particularly in children. However, separation anxiety disorder is characterized by excessive concern or worry about separation from loved ones. Individuals with separation anxiety disorder fear that something bad will happen to their loved ones while they are apart, leading to significant distress and impairment in daily functioning.
Phobias Phobias are intense, irrational fears of specific objects or situations. Common phobias include the fear of blood, needles, medical procedures involving injections, and agoraphobia (fear of crowded or public places). Phobias can be disruptive to daily life and may lead individuals to avoid certain situations or experiences.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is characterized by the presence of intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors or mental acts (compulsions). People with OCD often experience unwanted thoughts or images that cause anxiety and attempt to alleviate these feelings through repetitive rituals or actions. OCD can significantly impact daily functioning and may co-occur with other mental health conditions.